What If Humans Could Communicate via Brain-to-Brain Networks 2025
What If Humans Could Communicate via Brain-to-Brain Networks 2025
The idea of humans communicating through brain-to-brain networks might sound like a page out of a science fiction novel. But as technology advances, this concept is edging closer to reality. Imagine being able to send a thought directly to another person’s mind without saying a word, typing a message, or making a sound. In 2025, researchers are actively exploring the science behind this vision, blending neuroscience, artificial intelligence, and advanced communication systems.
This blog explores how such a futuristic communication system might work, its potential benefits, ethical implications, and what the science currently tells us about this mind-to-mind interface.
Understanding Brain-to-Brain Communication
To grasp how brain-to-brain networks might operate, we first need to understand the basics of brain communication. Our brains function using electrical signals and chemical messengers called neurotransmitters. Every thought, memory, or decision is encoded in complex patterns of neural activity. Brain-to-brain communication would involve decoding these patterns, translating them into signals, and sending them to another brain where the signal is decoded and experienced.
Researchers have already demonstrated rudimentary versions of this in labs. For example, studies have shown that brain signals from one animal can influence behavior in another, or that basic information like a simple yes or no can be transferred between human subjects using brain-computer interfaces (BCIs).
The Technology Behind the Vision
Several technologies would have to come together to enable brain-to-brain networks:
- Neural recording devices: These read brain activity in real time.
- Signal processing algorithms: These decode brain signals into digital language.
- Wireless transmission systems: These send the signal to another brain.
- Neural stimulation devices: These stimulate neurons in the recipient’s brain to reconstruct the original message or intent.
In 2025, we’re seeing rapid development in each of these areas. Companies and research institutions are building non-invasive BCIs that are safer and more practical than earlier versions. Meanwhile, AI is being used to improve signal decoding accuracy, allowing more complex thoughts or ideas to be recognized.
Real-World Applications
If brain-to-brain networks became a reality, the potential applications would be enormous:
- Education: Students could absorb information more efficiently by directly receiving it from instructors.
- Medical Communication: Patients with disabilities, such as those suffering from ALS or locked-in syndrome, could express themselves freely through thought.
- Teamwork and Collaboration: Teams could share complex ideas instantly, enhancing productivity in creative and scientific projects.
- Emergency Services: Instant silent communication between rescue workers or military personnel could save lives in critical situations.
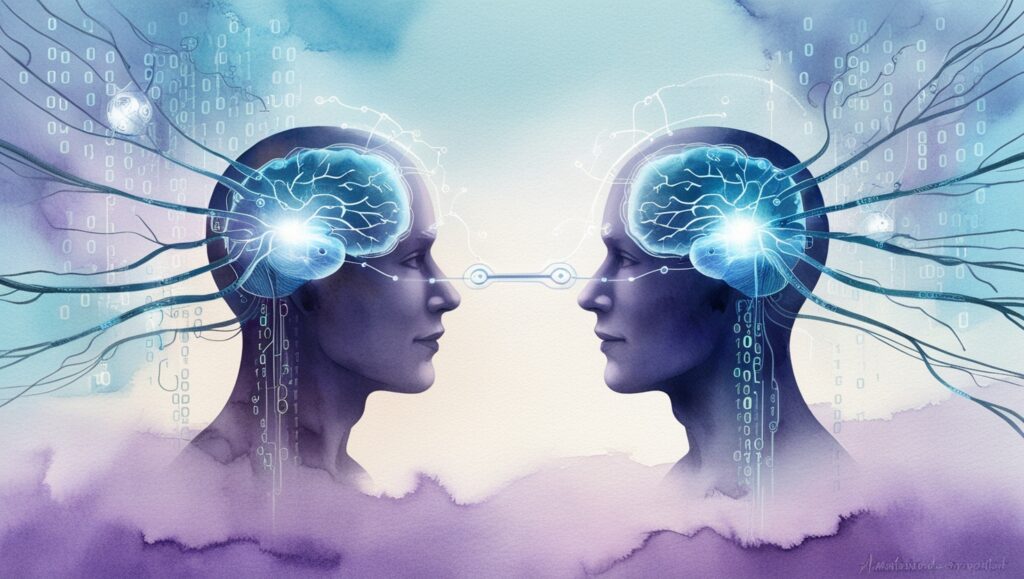



Ethical Considerations
With great power comes great responsibility. Direct brain communication raises serious ethical questions:
- Privacy: Could someone access your thoughts without permission?
- Security: What if someone hacks into your neural network?
- Consent: How do we ensure people aren’t forced into unwanted mental interactions?
- Identity: Would shared thought blur the line between individual minds?
Governments, ethicists, and scientists must work together to create regulations that protect people while enabling technological growth.
Challenges and Limitations
While the concept is fascinating, several major hurdles remain:
- Signal Complexity: Human thoughts are incredibly complex, and decoding them accurately is still difficult.
- Data Volume: Transmitting neural signals involves massive amounts of data. Efficient, real-time transmission is a technical challenge.
- Brain Variability: Each person’s brain is different. One person’s “neural code” won’t be the same as another’s.
- Psychological Effects: Receiving someone else’s thoughts could alter your own thinking patterns, raising questions about mental integrity and autonomy.
Are We Close to Achieving This?
In 2025, we’re not yet communicating entire thoughts or emotions directly from one brain to another. However, the groundwork is being laid. Experimental brain-to-brain communication between humans has already been demonstrated for simple tasks. Scientists are now working on expanding this to more complex forms of information.
Institutions like the University of Washington and companies like Neuralink are investing heavily in research that could one day make these mind-to-mind connections a reality.
A Future Connected by Minds
If this technology matures, it could usher in a new age of human connectivity. Relationships could deepen, misunderstandings could reduce, and collaboration could become almost frictionless. However, these possibilities come with the weight of deep ethical and social responsibility.
We must ask ourselves not only what is possible, but what is acceptable. Just as language shaped human history, brain-to-brain networks could redefine what it means to be human. But as with all powerful tools, the challenge lies in using it wisely.
—
If you’re interested in understanding more about how the brain works and how technology is shaping the future, check out the Wikipedia article on Brain–computer interface:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brain–computer_interface
—
Want to explore more of our thought-provoking blogs?
What If We Could Harness Energy from Black Holes
https://www.edgythoughts.com/what-if-we-could-harness-energy-from-black-holes-2025
What If Time Travel Became Scientifically Possible
https://www.edgythoughts.com/what-if-time-travel-became-scientifically-possible-2025